COVID 19 IS NOT THE ONLY THING THAT CAN KILL YOU.
OCTOBER BREAST CANCER AWARENESS MONTH
With everything going on in the world right now self-care is often let slide. As we discussed in our blog from November 2018, https://www.uniformsandscrubs.com/blog/self-care.html taking care of your self is not selfish.
We are working crazy long hours. Half the time we struggle with shortages of basic products and services. You are trying to take care of your patients at work and your family and friends at home, but who is going to take care of you?
October is Breast Cancer Awareness Month. So how about taking a few moments for some of that self care? First and foremost let’s remember that, though more common in women, breast cancer can affect anyone male or female. So guys don’t just blow by this post because you think it doesn’t apply to you. All doctors agree that early detection is the number one factor in surviving breast cancer. https://www.breastcancer.org/symptoms/testing/types/self_exam
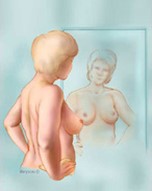
How to do a breast self-exam: The five steps
|
Step 1: Begin by looking at your breasts in the mirror with your shoulders straight and your arms on your hips.
Here's what you should look for: · Breasts that are their usual size, shape, and color · Breasts that are evenly shaped without visible distortion or swelling If you see any of the following changes, bring them to your doctor's attention: · Dimpling, puckering, or bulging of the skin · A nipple that has changed position or an inverted nipple (pushed inward instead of sticking out) · Redness, soreness, rash, or swelling |
Breast Self-Exam — Step 1 |
|
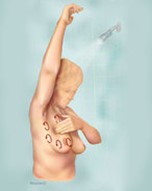
Step 2: Now, raise your arms and look for the same changes.
Step 3: While you're at the mirror, look for any signs of fluid coming out of one or both nipples (this could be a watery, milky, or yellow fluid or blood).
|
Breast Self-Exam — Steps 2 and 3 |
|
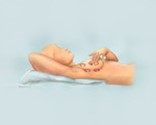
Step 4: Next, feel your breasts while lying down, using your right hand to feel your left breast and then your left hand to feel your right breast. Use a firm, smooth touch with the first few finger pads of your hand, keeping the fingers flat and together. Use a circular motion, about the size of a quarter.
Cover the entire breast from top to bottom, side to side — from your collarbone to the top of your abdomen, and from your armpit to your cleavage. Follow a pattern to be sure that you cover the whole breast. You can begin at the nipple, moving in larger and larger circles until you reach the outer edge of the breast. You can also move your fingers up and down vertically, in rows, as if you were mowing a lawn. This up-and-down approach seems to work best for most women. Be sure to feel all the tissue from the front to the back of your breasts: for the skin and tissue just beneath, use light pressure; use medium pressure for tissue in the middle of your breasts; use firm pressure for the deep tissue in the back. When you've reached the deep tissue, you should be able to feel down to your ribcage. |
Breast Self-Exam — Step 4 |
|
Step 5: Finally, feel your breasts while you are standing or sitting. Many women find that the easiest way to feel their breasts is when their skin is wet and slippery, so they like to do this step in the shower. Cover your entire breast, using the same hand movements described in step 4.
|
Breast Self-Exam — Step 5 |
What to do if you find a lump
Don’t panic if you think you feel a lump in your breast. Most women have some lumps or lumpy areas in their breasts all the time, and most breast lumps turn out to be benign (not cancer). There are a number of possible causes of non-cancerous breast lumps, including normal hormonal changes, a benign breast condition, or an injury.
Don’t hesitate to call your doctor if you’ve noticed a lump or other breast change that is new and worrisome. This is especially true for changes that last more than one full menstrual cycle or seem to get bigger or more prominent in some way. If you menstruate, you may want to wait until after your period to see if the lump or other breast change disappears on its own before calling your doctor. The best healthcare provider to call would be one who knows you and has done a breast exam on you before — for example, your gynecologist, primary care doctor, or a nurse practitioner who works with your gynecologist or primary care doctor.
Know what to expect. At an appointment to evaluate a breast lump, your doctor will take a health history and do a physical exam of the breast, and will most likely order breast imaging tests. Ultrasound is often the first or only imaging test used to evaluate a lump in women who are under age 30 or are pregnant or breastfeeding. Both an ultrasound and a mammogram are typically recommended to evaluate a lump in women who are over age 30 and not pregnant or breastfeeding. If further testing is needed, your doctor may recommend additional imaging with MRI (magnetic resonance imaging), MBI (molecular breast imaging), and/or a biopsy. He or she may also refer you to a breast specialist (typically, a breast surgeon) for further evaluation.
Make sure you get answers. It’s important that your doctor gives you an explanation of the cause of the lump or other breast change and, if necessary, a plan for monitoring it or treating it. If you’re not comfortable with the advice of the first doctor you see, don’t hesitate to get a second opinion.
How to make breast self-exam part of your breast cancer screening strategy
Make it routine. The more you examine your breasts, the more you will learn about them and the easier it will become for you to tell if something has changed. Try to get in the habit of doing a breast self-examination once a month to familiarize yourself with how your breasts normally look and feel. Examine yourself several days after your period ends, when your breasts are least likely to be swollen and tender. If you are no longer having periods, choose a day that's easy to remember, such as the first or last day of the month.
Get to know your breasts' different “neighborhoods.” The upper, outer area — near your armpit — tends to have the most prominent lumps and bumps. The lower half of your breast can feel like a sandy or pebbly beach. The area under the nipple can feel like a collection of large grains. Another part might feel like a lumpy bowl of oatmeal.
Start a journal where you record the findings of your breast self-exams. This can be like a small map of your breasts, with notes about where you feel lumps or irregularities. Especially in the beginning, this may help you remember, from month to month, what is “normal” for your breasts. It is not unusual for lumps to appear at certain times of the month, but then disappear, as your body changes with the menstrual cycle (if you are still menstruating).